-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:May 17. 2021, 14:49:49 Views:136
A long time ago, PCBs were made of cardboard and only had a single-sided function. However, nowadays, PCB manufacturers are innovating methods to make PCBs smaller in size, more durable and able to pack more power supplies. Over time, these changes have allowed PCBs to enter everyday consumer electronic products. In today's society, the use of PCBs is ubiquitous, which inspires an entire field of electrical engineers and hobbyists to create more complex designs.
The PCB manufacturing process is impressive, and even those who are familiar with PCB design may not understand all the details of the PCB manufacturing process. Learn more about the various PCB manufacturing techniques that take your design from a virtual image on a computer screen to a tangible green board in a toaster.
PCB manufacturing basis
Before delving into PCB manufacturing, it is important to understand the composition of the PCB. Usually, people will describe the PCB as a layered cake. The most basic PCB design has four layers: substrate (base), copper, solder mask and screen printing. All these layers work together and must be perfectly aligned for the final product to work.
After designing the PCB and sending the PCB design to the manufacturer, what will they do? For starters, they use your PCB design as a blueprint for the entire process.
Through hole method
One of the earliest forms of PCB manufacturing is the through-hole method. This time-tested method is quickly being replaced by more modern PCB manufacturing, which is called surface mount technology (SMT). Although each has advantages and disadvantages, PCBA factories seem to be able to produce smaller and cheaper PCB boards.
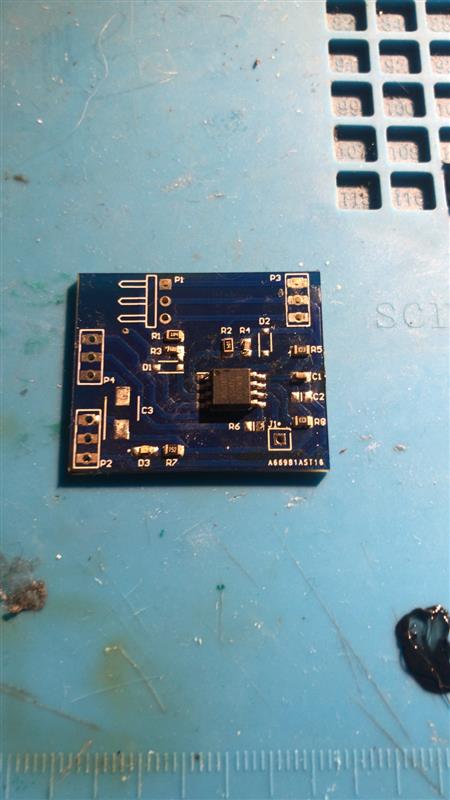

We will first look at the complex work involved in through-hole PCB design. The most significant difference in the through-hole method is that the manufacturer has drilled a hole in the board so that factory workers can double-check the alignment of each layer before proceeding to the next step. Using the through-hole method, the manufacturer will print your PCB design onto a special laminated paper. Once the design is captured on this special paper, the manufacturer can attach a thin copper sheet. This will be the basis of your substrate or PCB.
Create layer
The next step is to start processing the copper that will form the PCB layer. This process is somewhat similar to the way photos are developed, so that household PCB manufacturers will use the same processing chemicals. Essentially, the special laminated paper is covered with photosensitive chemicals, and when ultraviolet rays pass through, it hardens the desired area. This indicates which parts of the final PCB should be retained by the manufacturer according to your design, and which copper chips should be removed.
When the chemicals dry and harden, the board is washed with an alkaline solution and ready for inspection. If the circuit board is suitable for use, technicians can use powerful chemicals to remove unnecessary copper, leaving only the copper needed for the PCB design.
Next, the copper layers are laminated together. The technician must always pay attention to the details and always pay attention to the perfect alignment of each layer with the last layer. The result is a beautiful semi-finished board.
The factory can use the X-ray machine to find the location to be drilled, and then use the high-power drilling machine for precise processing. Finally, the plate is electroplated, and then a series of chemicals are fused in each layer. Before the solder mask is installed, the last etch will occur. This etching ensures that your PCB has the correct connections to achieve the creation function.
Surface mount technology
Surface mount technology (SMT) is becoming more and more common in the PCB manufacturing process because it can simplify mass production. Using SMT equipment, the PCB manufacturing process is more automated, so it is less prone to human error. The PCB designed by SMT does not have the protruding holes in the through-hole method. Briefly introduce the production methods of these PCBs.
Convenience of using steel mesh
By using high-performance computers and technology, machinery can complete your PCB design and create a steel mesh. The stencil contains all the information needed to automate the process to complete your design. The stencil also allows the machine to trace the solder paste onto the board only in designated areas.
The circuit board can now be run through the placement machine, which eliminates guesswork and errors in the PCB design process. The pick-and-place machine holds various components in its reel and reads the solder paste to place the appropriate components on the board in accordance with the instructions of the PCB design. The solder paste also fixes all parts in place so that the components will not be knocked off, which may cause product failure.
After this process is complete, heat the PCB and melt the solder paste to fuse the layers together. Then prepare for PCB cleaning to ensure that there is no residual solder paste on the board. Finally, the circuit board will be inspected for any potential defects.
Advantages of SMT placement technology
As you can see, SMT is a more direct and automated process. Its simplicity makes it most suitable for mass production of PCBs. Once the stencil is created for the design, countless circuit boards can be printed. Since the process relies on computers and machines rather than technicians, it is also less susceptible to human error. If the PCB board has an error, it may be because the pick and place machine needs to be reconfigured.
Another major advantage of SMT manufacturing is that they tend to allow higher density component placement while still maintaining smaller circuit boards. Since the circuit board is smaller, the travel distance of the connection is shorter, resulting in better power.
The biggest disadvantage of the steel mesh-based process is that the rapid production of prototypes is more challenging. This system works best if the same stencil is used repeatedly instead of creating a stencil that will change.
However, in view of the automation of the SMT process, it is no wonder that the SMT manufacturing method has achieved greater development in the PCB field than the through hole. No matter which route you take, make sure you understand the PCB manufacturing process used by the manufacturer. In today's world, everything becomes faster and smaller, you need to make a decision to bring you the best return on investment.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com


We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:
Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
