-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Nov 05. 2021, 16:21:34 Views:195
There is a key component in the electronics industry called PCB (printed circuit board). This is a too basic component, which makes it difficult for many people to explain what a PCB is. This article will explain the composition of PCB in detail, as well as some commonly used terms in the field of PCB.
In the next few pages, we will discuss the composition of the PCB, including some terminology, a brief assembly method, and an introduction to the PCB design process.
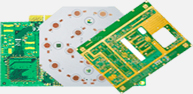
What's a PCB?
PCB (Printed circuit board) is the most common name, and it can also be called "printed wiring boards" or "printed wiring cards". Before the advent of the PCB, the circuit was composed of point-to-point wiring. The reliability of this method is very low, because as the circuit ages, the rupture of the circuit will cause the circuit node to open or short circuit.
Winding technology is a major advancement in circuit technology. This method improves the durability and replaceability of the circuit by winding small-diameter wires on the poles at the connection point.
As the electronics industry develops from vacuum tubes and relays to silicon semiconductors and integrated circuits, the size of electronic components has decreased and the prices have also fallen. Electronic products appear more and more frequently in the consumer field, prompting manufacturers to find smaller and more cost-effective solutions. Thus, the PCB was born.
Composition
The PCB looks like a multi-layer cake or lasagna--the layers of different materials are pressed together by heat and adhesive.
Let's start from the middle level.
FR4
The substrate of PCB is generally glass fiber. In most cases, the glass fiber substrate of PCB generally refers to the material "FR4". The solid material "FR4" gives the PCB hardness and thickness. In addition to the FR4 substrate, there are flexible circuit boards produced on flexible high-temperature plastics (polyimide or similar) and so on.
You may find PCBs with different thicknesses; however, the thickness of SparkFun's products is mostly 1.6mm (0.063’’). Some products also use other thicknesses, such as LilyPad and Arudino Pro Micro boards with a thickness of 0.8mm.
Inexpensive PCBs and hole boards (see the picture above) are made of materials such as epoxy resin or phenol, which lack the durability of FR4, but are much cheaper. When soldering things on this kind of board, you will smell a lot of peculiar smell. This type of substrate is often used in very low-end consumer products. Phenolic substances have a low thermal decomposition temperature, too long welding time will cause them to decompose and carbonize, and emit an unpleasant smell.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com


We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:
Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
