-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
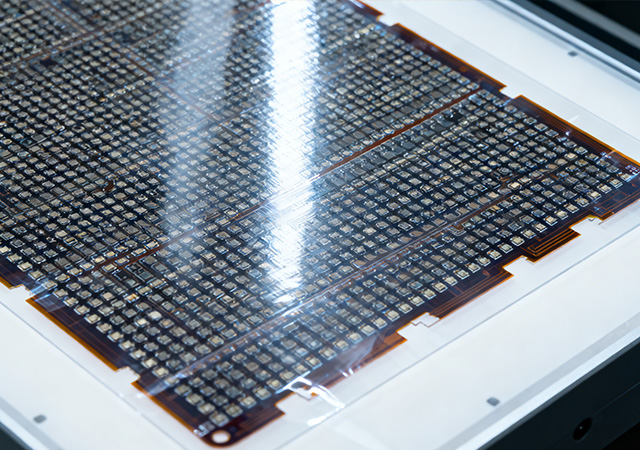
The global electronics industry’s unrelenting pursuit of miniaturization, multi-functionality, and energy efficiency has positioned FPC High Density Component Assembly as a transformative manufacturing technology. This specialized process focuses on integrating a high concentration of electronic components—including active devices, passive components, and functional modules—onto flexible printed circuits (FPCs) while maintaining mechanical flexibility and electrical reliability. Unlike standard FPC assembly, which prioritizes basic component connectivity, FPC High Density Component Assembly emphasizes optimizing interconnect density, thermal management, and assembly consistency to support the next generation of compact, high-performance devices. For industries spanning 5G communications, electric vehicles (EVs), and advanced medical equipment, this assembly technology is a critical enabler of product innovation and market competitiveness.
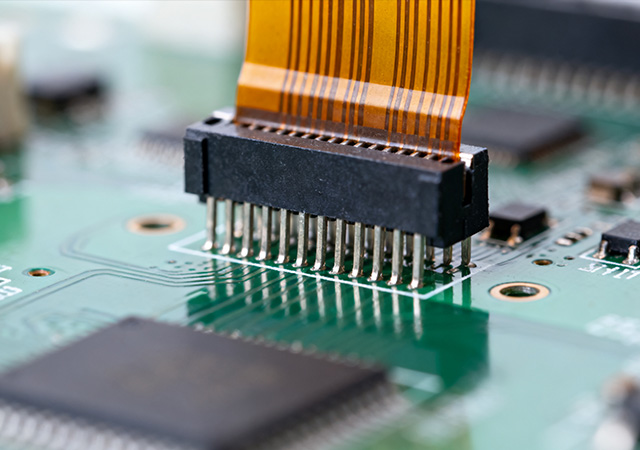
As high-end electronic devices evolve toward miniaturization, intelligence, and high performance, the demand for Precision Component FPC Assembly Service has surged dramatically. This specialized service focuses on the accurate assembly of micro-sized, high-precision components—such as microcontrollers, precision sensors, and ultra-small passive components—onto flexible printed circuits (FPCs). Unlike standard FPC assembly, which prioritizes basic connectivity, Precision Component FPC Assembly Service requires rigorous control over component placement accuracy, solder joint integrity, and FPC substrate stability to ensure optimal performance of high-end devices. For industries including precision medical equipment, aerospace electronics, and premium consumer gadgets, this service is a critical cornerstone for translating innovative designs into reliable, market-ready products.
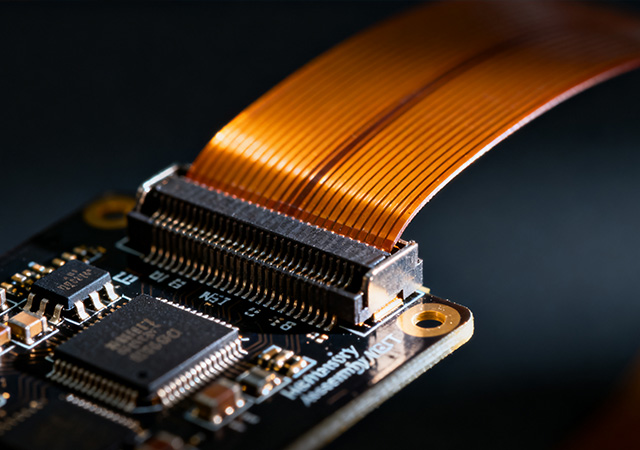
As electronic devices trend toward ultra-miniaturization, high functionality, and flexible form factors, High Density SMT FPC Assembly has emerged as a critical technology in advanced electronic manufacturing. This specialized assembly process combines the precision of high-density surface mount technology (SMT) with the flexibility of flexible printed circuits (FPCs), enabling the integration of hundreds of tiny components—such as microchips, resistors, and capacitors—onto flexible substrates. Unlike traditional rigid PCB SMT assembly, High Density SMT FPC Assembly requires unique expertise in handling flexible materials, controlling thermal stress, and ensuring precise component placement. For industries ranging from consumer electronics to medical devices and automotive systems, this assembly technology is a key enabler of products that balance compact design, high performance, and mechanical adaptability.
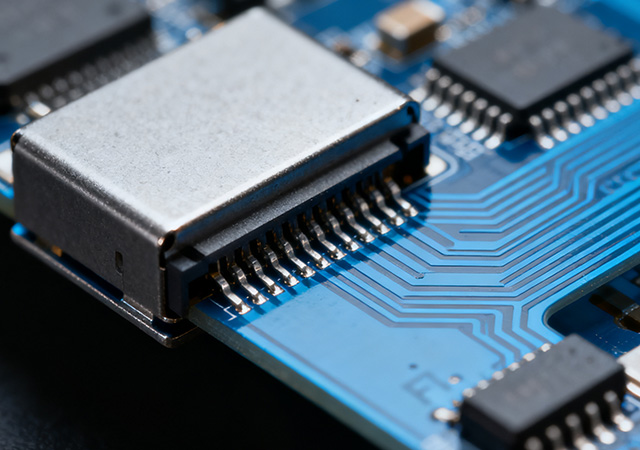
The global electronics industry’s shift toward flexibility, miniaturization, and intelligent integration has elevated the status of professional FPC manufacturers from mere component suppliers to strategic innovation partners. An FPC manufacturer specializes in the research, development, and production of flexible printed circuits (FPCs)—versatile components that enable seamless integration of electronic functions in constrained, curved, or dynamic environments. Unlike rigid PCB manufacturers, FPC manufacturers possess unique expertise in balancing mechanical flexibility with electrical performance, catering to the diverse needs of industries ranging from consumer electronics to industrial automation. For enterprises aiming to develop cutting-edge electronic products, partnering with a reputable FPC manufacturer is essential to translating design concepts into reliable, market-ready solutions.
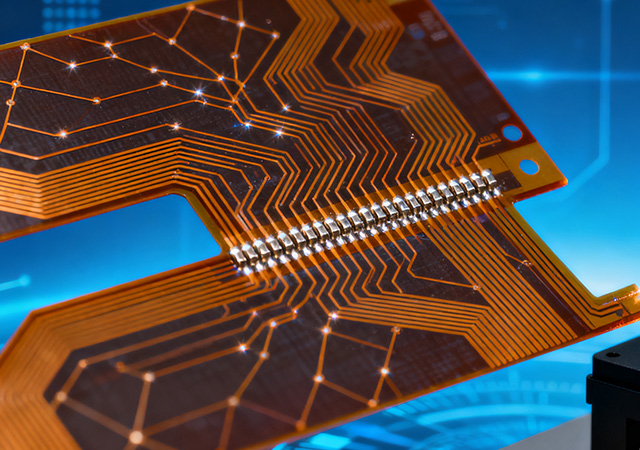
As high-end electronics continue to pursue miniaturization, high integration, and stable performance, the role of a professional HDI FPC Manufacturer has become increasingly vital in the global supply chain. An HDI FPC Manufacturer specializes in the design, development, and mass production of high-density interconnect flexible printed circuits (HDI FPCs), which are essential components for devices requiring compact layouts, high-speed signal transmission, and flexible installation. Unlike general FPC manufacturers, HDI FPC manufacturers possess specialized capabilities in balancing high-density routing with mechanical flexibility, ensuring that their products meet the stringent requirements of industries such as 5G communications, automotive electronics, and precision medical devices. For enterprises aiming to launch innovative electronic products, partnering with a reputable HDI FPC Manufacturer is a critical step to ensure production efficiency, product reliability, and market compe

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com


We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:
Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
