-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
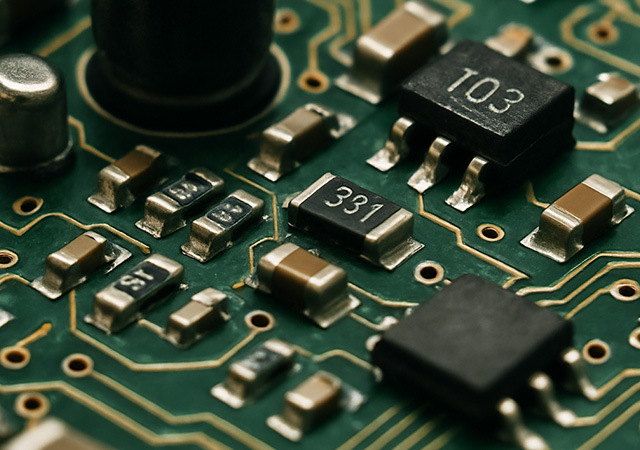
Discover the benefits of flex PCB assembly techniques that enhance electronic device efficiency with improved durability, performance, and cost savings.
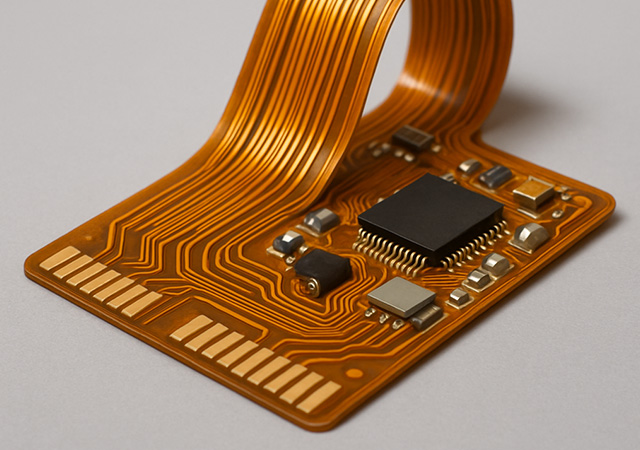
Discover the benefits of high-density flex PCB assembly, essential for modern electronics. Learn about PCB fabrication, assembly services, and industry applications.
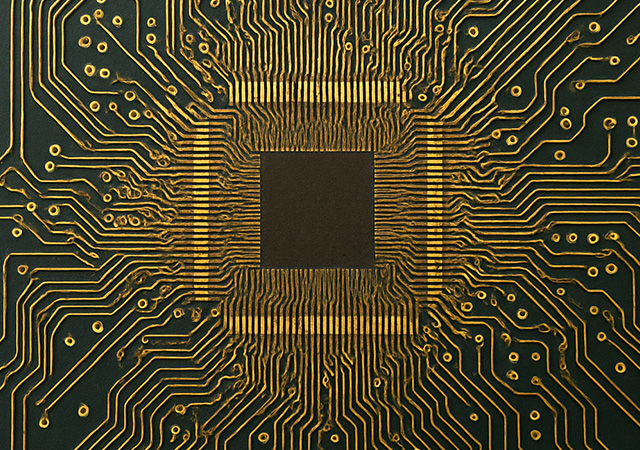
Discover the benefits of high-density flex PCB assembly, essential for modern electronics. Learn about PCB fabrication, assembly services, and industry applications.
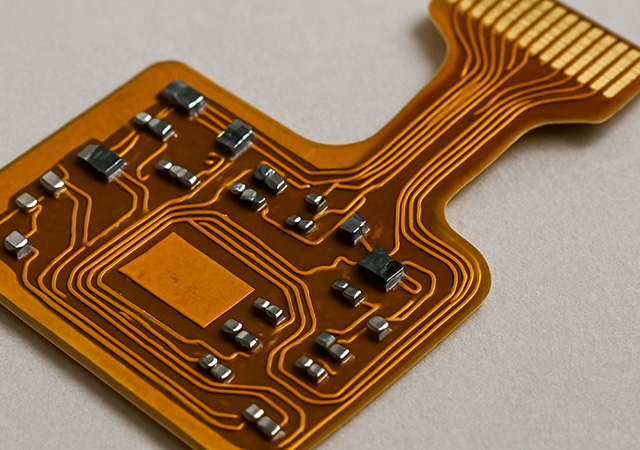
Discover the benefits of wearable flex PCB assembly services for creating innovative, compact, and reliable wearable technology. Enhance your device design today!
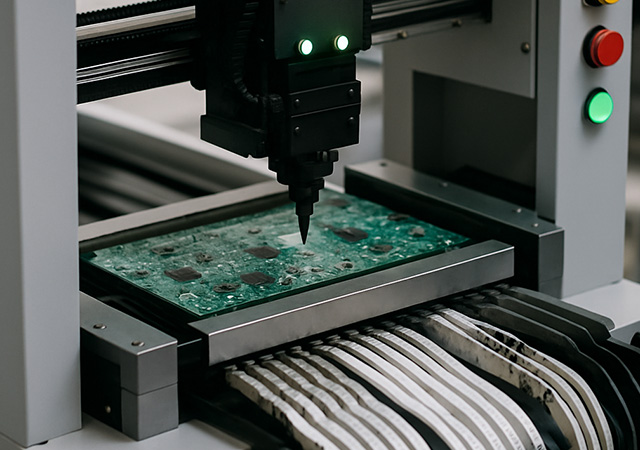

Explore the essential PCB assembly process, from solder paste application to final testing, ensuring efficient and reliable electronic devices.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com


We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:
Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
