-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
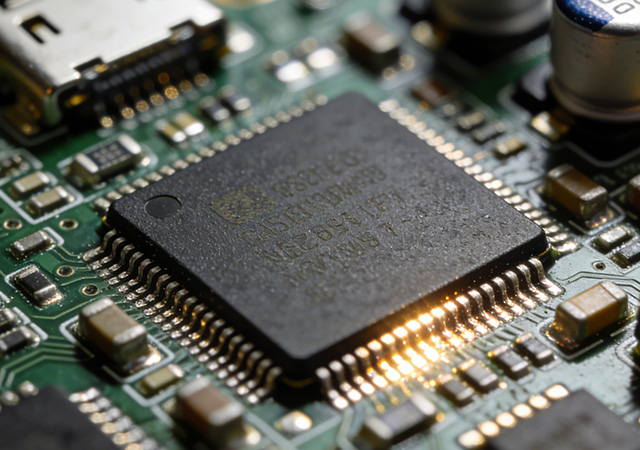
In the global flexible printed circuit (FPC) industry, quality consistency and reliability are the cornerstones of long-term cooperation between suppliers and clients. An ISO 9001 Flexible PCB Supplier distinguishes itself by adhering to the rigorous requirements of the ISO 9001 quality management system, integrating systematic quality control into every link of FPC design, production, and service. Unlike non-certified suppliers that rely on fragmented quality checks, ISO 9001-certified suppliers establish standardized, traceable, and continuously improved quality processes, ensuring that each batch of FPC products meets predefined quality benchmarks. For electronics brands pursuing global market expansion and high-quality product strategies, partnering with an ISO 9001 Flexible PCB Supplier is critical to mitigating quality risks, simplifying compliance audits, and building end-user trust.
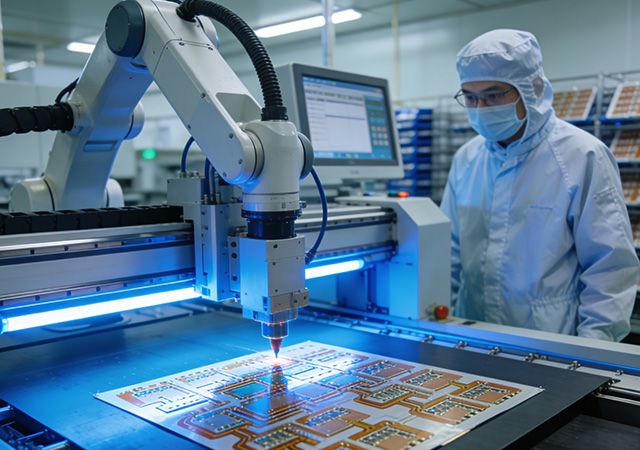

In the fast-evolving electronics industry, flexible printed circuits (FPCs) are increasingly deployed in high-precision, high-reliability applications such as aerospace, advanced medical devices, and next-gen consumer electronics. A professional FPC manufacturer stands out through its robust advanced testing validation systems and proactive cutting-edge technology research capabilities, ensuring FPC products meet the stringent performance requirements of emerging applications while driving industry technological progress. Unlike conventional FPC producers that focus solely on production, leading manufacturers prioritize the entire lifecycle reliability of FPCs and invest in forward-looking technology R&D, providing clients with not only qualified products but also long-term technical competitiveness. For electronics brands pursuing innovation and high-quality development, partnering with an FPC manufacturer with excellent testing capabilities and technological foresight is a strategic
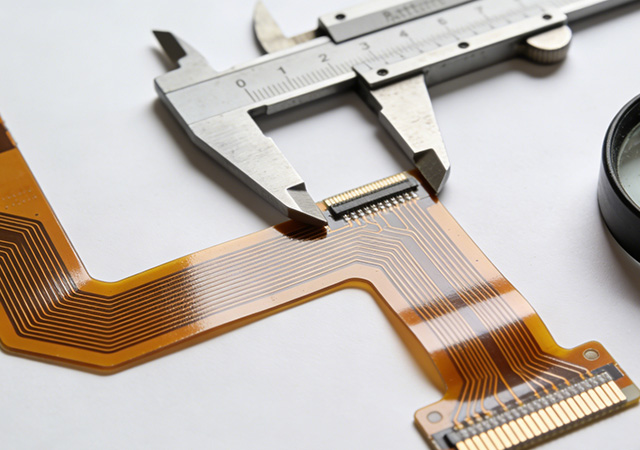
Batteries serve as the backbone of modern energy systems, spanning lithium-ion, lead-acid, nickel-metal hydride, and emerging solid-state variants, with applications ranging from consumer electronics and electric vehicles (EVs) to industrial energy storage and renewable energy integration. A professional Batteries FPC Manufacturer distinguishes itself by delivering flexible printed circuits (FPCs) that adapt to the unique operational requirements of diverse battery types, while emphasizing modular integration and system-level compatibility. Unlike niche FPC suppliers focused on single battery categories, these manufacturers excel in cross-battery-type customization, enabling seamless connectivity between battery cells, management systems, and end-use devices. For brands operating across multiple battery-powered sectors, partnering with a versatile Batteries FPC Manufacturer is critical to streamlining supply chains, ensuring product consistency, and driving innovation in energy storage
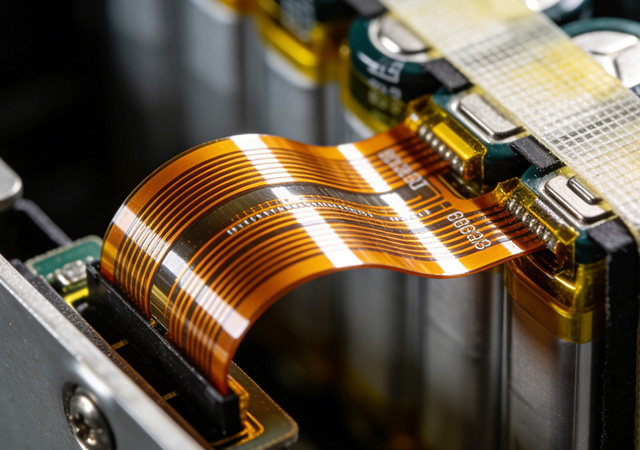
Lithium batteries have become the dominant power source for electric vehicles (EVs), energy storage systems, portable electronics, and renewable energy integration, thanks to their high energy density, long cycle life, and lightweight advantages. A professional Lithium Battery FPC Manufacturer plays a crucial role in unlocking the full performance potential of lithium battery systems by engineering flexible printed circuits (FPCs) tailored to the unique electrochemical and operational characteristics of lithium batteries. Unlike generic battery FPC suppliers, these specialized manufacturers focus on addressing lithium battery-specific challenges—such as stable current transmission during high-rate charging/discharging, compatibility with lithium battery chemistry, and long-term reliability under cyclic load conditions. For brands developing high-performance lithium battery products, partnering with a reputable Lithium Battery FPC Manufacturer is essential to ensuring system efficiency,
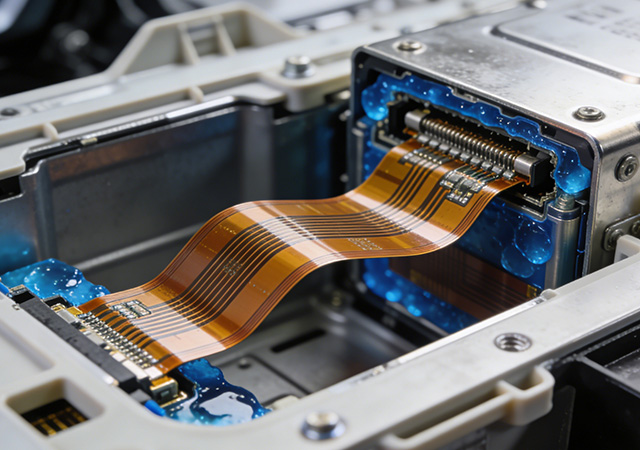
Battery systems are the core power source for new energy vehicles (NEVs), energy storage systems, portable electronics, and medical devices, where safety is non-negotiable. A professional High Safety Battery FPC Supplier plays a pivotal role in ensuring battery operational safety by engineering flexible printed circuits (FPCs) with specialized protective designs, material selection, and performance optimization. Unlike generic FPC suppliers, these specialized providers focus on addressing battery-specific safety risks—such as overcurrent, overheating, short circuits, and insulation failure—while maintaining the flexibility and integration efficiency required for modern battery packs. For brands developing high-reliability battery products, partnering with a reputable High Safety Battery FPC Supplier is critical to mitigating safety hazards and meeting stringent industry safety standards.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com


We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:
Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
